Health insurance is a critical component of managing personal and family healthcare needs. It provides financial protection against high medical costs and ensures access to necessary medical services. With numerous health insurance options available, understanding the different types of plans can help you make informed decisions tailored to your healthcare needs and financial situation. This article delves into the various types of health insurance plans, outlining their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
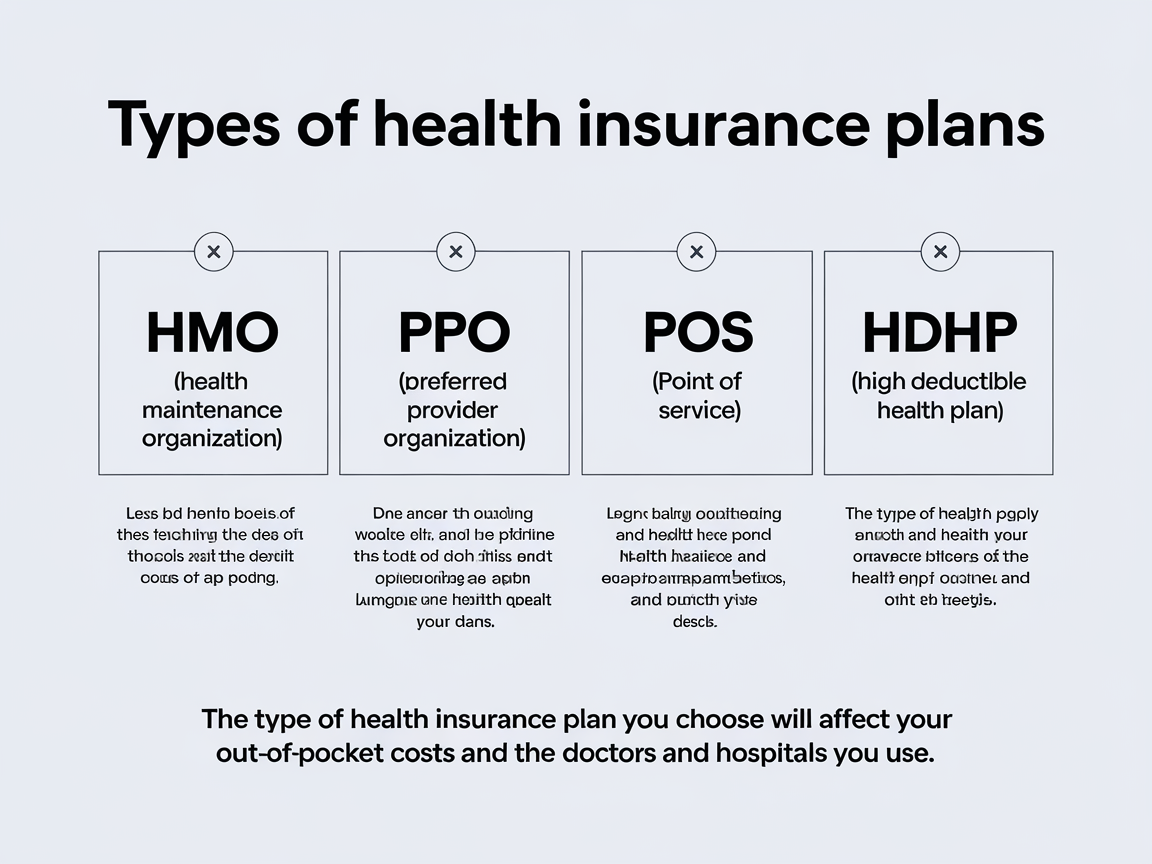
1. Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
Overview
HMO plans are designed to provide a range of healthcare services through a network of providers. Members are required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and need referrals to see specialists.
Features
- Network of Providers: HMO plans operate within a specific network. Care outside this network is typically not covered, except in emergencies.
- Lower Premiums: Generally, HMO plans have lower monthly premiums compared to other types of plans.
- Emphasis on Preventive Care: HMO plans often cover preventive services with no out-of-pocket costs.
Advantages
- Lower costs for premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Coordinated care through a primary care physician.
- Emphasis on preventive care reduces the risk of chronic conditions.
Disadvantages
- Limited flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- Need for referrals can be cumbersome for some patients.
- Out-of-network care is rarely covered.
2. Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)

Overview
PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Members can see any doctor or specialist without a referral, but there are incentives for using providers within the network.
Features
- Flexibility: Members can choose to receive care from both in-network and out-of-network providers.
- Higher Premiums: PPO plans typically have higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to HMO plans.
- No Referrals Needed: Members do not need referrals to see specialists.
Advantages
- Greater choice of healthcare providers.
- No referral requirement simplifies access to specialists.
- Coverage for out-of-network care, albeit at a higher cost.
Disadvantages
- Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Complexity in understanding costs associated with in-network versus out-of-network care.
3. Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)

Overview
EPO plans combine elements of HMO and PPO plans. They require members to use a network of providers but do not require referrals to see specialists.
Features
- Network Restrictions: EPO plans typically do not cover out-of-network care, except in emergencies.
- No Referrals: Members can see any specialist within the network without needing a referral.
- Lower Premiums than PPOs: EPOs usually have lower premiums compared to PPOs but higher than HMOs.
Advantages
- No referrals make accessing specialists easier.
- Lower premiums compared to PPOs.
- Focus on in-network providers can lead to better coordination of care.
Disadvantages
- Limited provider network can be restrictive.
- No coverage for out-of-network care.
4. Point of Service (POS)
Overview
POS plans blend features of HMO and PPO plans. Members choose a primary care physician and need referrals to see specialists, but they can also see out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
Features
- PCP Requirement: Like HMOs, members must select a primary care physician.
- Referral Requirement: Referrals are needed to see specialists within the network.
- Out-of-Network Options: Members can seek care outside the network, usually at a higher cost.
Advantages
- Flexibility to see out-of-network providers, albeit at a cost.
- Coordination of care through a primary care physician.
Disadvantages
- Need for referrals can be inconvenient.
- Higher costs for out-of-network care.
5. High Deductible Health Plans (HDHP)
Overview
HDHPs are plans that feature higher deductibles and lower premiums. They are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) that allow members to save money tax-free for medical expenses.
Features
- High Deductibles: Members pay a higher deductible before the insurance starts covering costs.
- Lower Premiums: Monthly premiums are generally lower compared to traditional plans.
- Health Savings Account (HSA) Eligibility: Members can contribute to an HSA for tax-free savings.
Advantages
- Lower premiums can make healthcare more affordable.
- HSAs provide tax advantages and can be used for various medical expenses.
- Encourages members to shop for healthcare services.
Disadvantages
- High out-of-pocket costs before insurance kicks in.
- May not be suitable for those with chronic health conditions requiring regular care.
6. Catastrophic Health Insurance

Overview
Catastrophic plans are designed for young, healthy individuals. They offer lower premiums but have high deductibles and are intended to protect against major medical expenses.
Features
- Low Premiums: Monthly premiums are generally lower compared to other plans.
- High Deductibles: Members must pay a high deductible before coverage starts.
- Coverage for Essential Health Benefits: Catastrophic plans cover essential health benefits after the deductible is met.
Advantages
- Affordable premiums make it an attractive option for young individuals.
- Provides a safety net for major medical expenses.
Disadvantages
- High deductibles can make it costly for routine healthcare needs.
- Limited coverage before the deductible is met.
7. Medicare
Overview
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, but it also covers certain younger individuals with disabilities.
Features
- Part A (Hospital Insurance): Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice, and some home health care.
- Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers outpatient care, preventive services, and some home health care.
- Part C (Medicare Advantage): Combines Parts A and B and often includes additional benefits, such as vision and dental coverage.
- Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Provides prescription drug coverage.
Advantages
- Comprehensive coverage for seniors and disabled individuals.
- Variety of plans, including Medicare Advantage, offer additional benefits.
Disadvantages
- May involve premiums, deductibles, and copayments.
- Coverage can vary by plan, and not all services are included.
8. Medicaid
Overview
Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage for individuals and families with low income. Eligibility and benefits vary by state.
Features
- Income-Based Eligibility: Coverage is available for low-income individuals, families, children, pregnant women, the elderly, and people with disabilities.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Medicaid covers a broad range of healthcare services, including hospital stays, outpatient services, long-term care, and preventive care.
Advantages
- Low or no cost for eligible individuals.
- Comprehensive coverage for necessary healthcare services.
Disadvantages
- Eligibility requirements can be complex.
- Limited provider options in some areas.
9. Short-Term Health Insurance
Overview
Short-term health insurance provides temporary coverage for individuals who are in between plans or need temporary protection.
Features
- Limited Duration: Policies are typically available for up to 12 months, with the possibility of renewal.
- Lower Premiums: Monthly premiums are usually lower than traditional health plans.
- Limited Benefits: Coverage may not include essential health benefits and may exclude pre-existing conditions.
Advantages
- Affordable option for temporary coverage.
- Quick enrollment process.
Disadvantages
- Limited benefits may not cover essential healthcare needs.
- Not a substitute for comprehensive health insurance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right health insurance plan involves understanding the different types available and assessing your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences. Each plan type offers unique features, benefits, and limitations, making it essential to evaluate them carefully.
By considering factors like premiums, deductibles, provider networks, and coverage options, you can select a health insurance plan that best fits your lifestyle and ensures access to necessary medical care.
FAQs
1. What is the best type of health insurance plan?
The best type of plan depends on individual needs, including healthcare usage, budget, and preferences for provider flexibility.
2. Can I switch health insurance plans?
Yes, you can switch plans during open enrollment periods or if you experience qualifying life events.
3. Are preventative services covered by all health insurance plans?
Most plans cover preventive services, but specifics can vary, so it’s essential to check individual plan details.
4. How do I know if a provider is in-network?
You can check your insurance provider’s website or contact customer service for a list of in-network providers.
5. What should I do if my claim is denied?
Review your insurance policy for coverage details, and follow your insurer’s appeal process to contest the denial.