Understanding Psychological Stress: Causes, Effects, and Management Strategies
"Finding calm in the chaos: Embrace mindfulness for a stress-free life."
Introduction
Psychological stress is a common experience in today’s fast-paced world, impacting individuals across various age groups, professions, and backgrounds. While a certain level of stress can be motivating, chronic stress can have severe consequences on mental and physical health. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of psychological stress, including its causes, effects, and effective management strategies.
What is Psychological Stress?
Psychological stress refers to the emotional and mental strain or tension that arises when individuals perceive challenges, demands, or threats that exceed their coping resources. It can be triggered by various factors, including personal, environmental, and social pressures. Understanding the nature of stress is crucial for recognizing its effects and developing effective coping mechanisms.
The Stress Response
When faced with stressors, the body undergoes a series of physiological changes known as the stress response. This response, often referred to as the “fight-or-flight” response, is initiated by the hypothalamus in the brain, leading to the release of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones prepare the body to react to perceived threats by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and energy levels.
Types of Stress
- Acute Stress: This is short-term stress that arises from specific events or situations, such as a job interview or an upcoming exam. Acute stress can be exhilarating and motivating but may lead to anxiety if experienced frequently.
- Chronic Stress: This type of stress persists over a longer period, often due to ongoing challenges such as financial difficulties, relationship issues, or workplace pressures. Chronic stress can lead to serious health problems if left unaddressed.
- Eustress vs. Distress: Eustress refers to positive stress that motivates and energizes individuals, while distress refers to negative stress that can lead to anxiety and health issues.
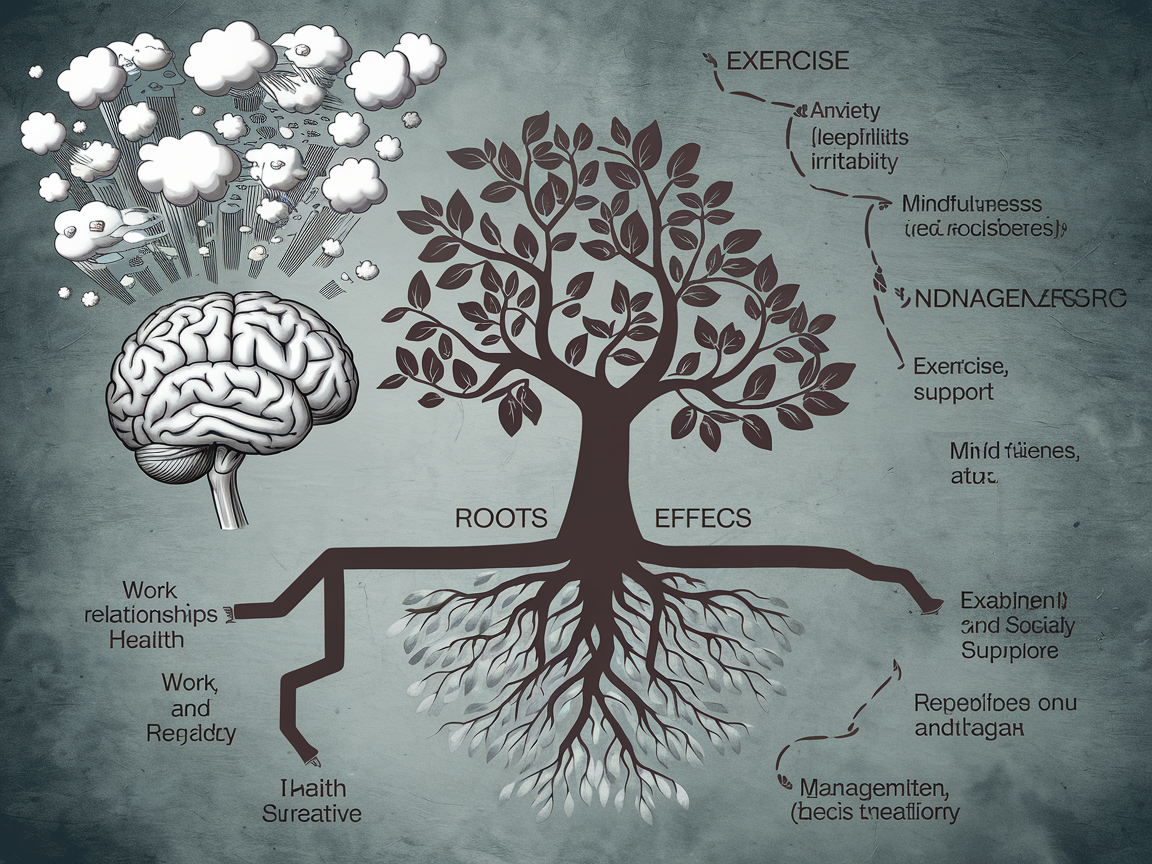
Causes of Psychological Stress

Understanding the causes of psychological stress is essential for identifying potential triggers in one’s life. Common causes include:
1. Life Changes
- Significant life events such as marriage, divorce, job loss, or the death of a loved one can lead to feelings of overwhelm and stress.
2. Work-related Pressures
- High workloads, tight deadlines, job insecurity, and conflicts with colleagues can contribute to work-related stress.
3. Financial Strain
- Financial difficulties, such as debt or unexpected expenses, can cause significant psychological stress and anxiety.
4. Relationship Issues
- Interpersonal conflicts, communication breakdowns, and unhealthy relationships can lead to emotional distress.
5. Health Concerns
- Chronic illnesses, injuries, or mental health disorders can create stress due to the emotional and physical challenges they present.
6. Academic Pressure
- Students often experience stress related to academic performance, exams, and the pressure to succeed.
7. Environmental Factors
- Noise, pollution, overcrowding, and natural disasters can also contribute to psychological stress.
Effects of Psychological Stress

The effects of psychological stress can be profound, impacting both mental and physical health. Some common effects include:
1. Mental Health Issues
- Chronic stress can lead to anxiety disorders, depression, and other mental health conditions. Individuals may experience persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or irritability.
2. Cognitive Impairment
- Stress can impair cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and decision-making. Individuals under stress may find it difficult to concentrate or think clearly.
3. Physical Health Problems
- Long-term stress can contribute to various physical health issues, such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes, and gastrointestinal problems.
4. Sleep Disturbances
- Stress often disrupts sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or poor-quality sleep, which can further exacerbate feelings of stress and fatigue.
5. Behavioral Changes
- Individuals may engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as substance abuse, overeating, or withdrawal from social interactions.
Recognizing the Signs of Psychological Stress

Recognizing the signs of psychological stress is the first step toward effective management. Common signs include:
1. Emotional Symptoms
- Feelings of anxiety, irritability, mood swings, and sadness.
2. Physical Symptoms
- Headaches, fatigue, muscle tension, gastrointestinal issues, and changes in appetite.
3. Cognitive Symptoms
- Difficulty concentrating, indecisiveness, and forgetfulness.
4. Behavioral Symptoms
- Changes in sleep patterns, withdrawal from social activities, and neglect of responsibilities.
Strategies for Managing Psychological Stress

Effective stress management is crucial for maintaining mental and physical well-being. Here are several strategies to cope with psychological stress:
1. Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
- Mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and promote a sense of calm.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
- Exercise is a powerful stress reliever. Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce anxiety.
3. Establish a Healthy Routine
- Maintaining a balanced routine that includes adequate sleep, nutritious meals, and regular physical activity can help mitigate stress levels.
4. Connect with Others
- Building and maintaining strong social connections can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation. Talking to friends or family about your feelings can be beneficial.
5. Set Realistic Goals
- Break tasks into manageable steps and set achievable goals. Celebrate small accomplishments to build confidence and motivation.
6. Limit Exposure to Stressors
- Identify stress triggers and, where possible, minimize exposure to them. This may involve setting boundaries at work or limiting time spent on social media.
7. Seek Professional Help
- If stress becomes overwhelming, seeking help from a mental health professional can provide valuable support and guidance. Therapy can equip individuals with coping strategies and tools for managing stress.
8. Practice Self-Care
- Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as hobbies, reading, or spending time in nature. Prioritizing self-care can rejuvenate the mind and body.
9. Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
- Replace unhealthy habits (like substance abuse) with healthier alternatives, such as journaling, art, or other creative outlets.
10. Educate Yourself about Stress
- Understanding stress and its effects can empower individuals to recognize their experiences and seek appropriate help.
Conclusion
Psychological stress is a prevalent issue that can have far-reaching effects on individuals’ lives. By understanding its causes, recognizing its signs, and implementing effective management strategies, individuals can take control of their mental well-being. Prioritizing mental health is essential for living a fulfilling and balanced life. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, and you are not alone in facing these challenges.
FAQs about Psychological Stress
1. What is psychological stress?
Psychological stress is a mental and emotional response to perceived challenges or threats that exceed an individual’s coping abilities. It can arise from various sources, including work, relationships, and life changes.
2. What are common causes of psychological stress?
Common causes include life changes (like marriage or divorce), work-related pressures, financial difficulties, health concerns, academic pressure, and interpersonal conflicts.
3. What are the signs of psychological stress?
Signs of psychological stress can include emotional symptoms (like anxiety and irritability), physical symptoms (such as headaches and fatigue), cognitive symptoms (difficulty concentrating), and behavioral changes (like withdrawal from social activities).
4. How does psychological stress affect physical health?
Chronic psychological stress can lead to various health issues, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes, and gastrointestinal problems. It can also disrupt sleep patterns and weaken the immune system.
5. What are effective strategies for managing psychological stress?
Effective strategies include practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy routine, connecting with others, setting realistic goals, and seeking professional help if needed.
6. When should I seek professional help for stress?
You should seek professional help if stress becomes overwhelming, interferes with daily life, or leads to persistent feelings of anxiety or depression. A mental health professional can provide valuable support and coping strategies.
7. Can stress ever be beneficial?
Yes, a certain level of stress (known as eustress) can be motivating and help individuals perform better in challenging situations. However, chronic stress is detrimental to health and well-being.
8. How can I recognize if I am experiencing chronic stress?
Chronic stress can be recognized by ongoing feelings of anxiety, irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating over an extended period. If these symptoms persist, consider consulting a professional.
9. Are there any physical symptoms associated with psychological stress?
Yes, physical symptoms can include headaches, muscle tension, fatigue, gastrointestinal issues, and changes in appetite or weight.
10. What role does exercise play in stress management?
Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Regular physical activity can help reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being.




